Gynecomastia vs Pseudogynecomastia: What Is the Difference?

Key Takeaways
- Gynecomastia involves excess glandular breast tissue caused by hormonal imbalances, while pseudogynecomastia is caused by fat accumulation in the chest area
- The main difference between gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia is that gynecomastia results from glandular tissue growth due to hormonal changes, whereas pseudogynecomastia is primarily due to excess fat without glandular enlargement.
- Gynecomastia feels firm and rubbery under the nipple, whereas pseudogynecomastia feels soft and uniformly fatty throughout the chest
- True gynecomastia requires surgical excision of glandular tissue, while pseudogynecomastia can often be treated with liposuction or lifestyle changes
- Accurate diagnosis by a board-certified plastic surgeon is essential for determining the most effective treatment approach
- Both conditions can significantly impact self-confidence and quality of life, making proper treatment important regardless of the underlying cause
Understanding Male Breast Enlargement: The Basics
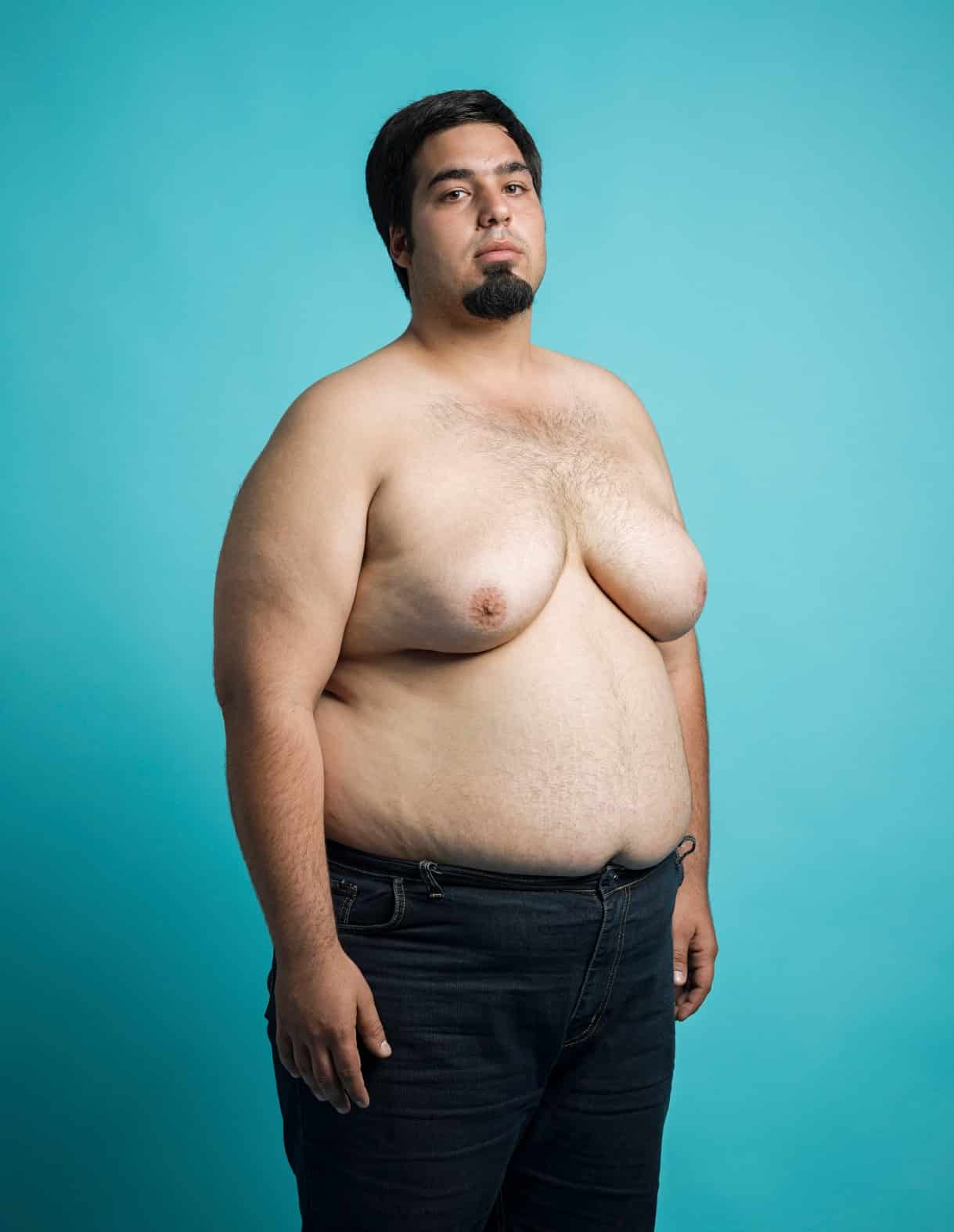
Enlarged male breasts affect millions of men worldwide, creating a condition that can significantly impact self-confidence and quality of life. Many men experience emotional and social distress due to the appearance of their chests, often feeling embarrassed or reluctant to show their bodies in public. While both gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia result in male breast enlargement that appears similar from the outside, understanding the key differences between these conditions is crucial for determining the most effective treatment approach.

The visual appearance of enlarged chests in men can be virtually identical, whether caused by excess glandular tissue or excess fatty tissue. These conditions can negatively affect men’s confidence in their bodies, leading to self-consciousness and lower self-esteem. However, the underlying causes, tissue composition, and optimal treatments differ significantly between these two conditions. Many patients struggle to understand which condition they have, leading to confusion about treatment options and realistic expectations.
Proper diagnosis is essential because the treatments differ significantly. Unlike gynecomastia, which requires surgical intervention to remove glandular breast tissue, pseudogynecomastia may respond to weight loss and lifestyle modifications. Statistics show that gynecomastia affects approximately 30-65% of males at some point in their lives, with three distinct peaks during the neonatal period, adolescence, and older adulthood.
What Is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is defined as the benign proliferation of glandular breast tissue in males, resulting from an imbalance between estrogen and androgen activity in the body. This condition involves the development of actual breast tissue rather than simply fat accumulation, creating a firm, rubbery mass typically located directly beneath the nipple-areolar complex.
The excess glandular tissue in gynecomastia feels distinctly different from fat tissue. During physical examination, patients and doctors can palpate a firm, sometimes disc-shaped mass of glandular breast tissue behind one or both nipples. This tissue may be tender or sensitive to touch, particularly in the early stages of development when inflammation and swelling are most pronounced.
True gynecomastia often presents with additional symptoms beyond visible enlargement. Many patients experience breast tenderness, swelling, and occasionally nipple discharge. The condition can affect one or both breasts, and asymmetry is common, with one side developing more excess breast tissue than the other. Unlike fatty tissue, this glandular tissue cannot be reduced through diet and exercise alone.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Hormonal imbalance serves as the primary driver of gynecomastia development. When estrogen levels increase relative to testosterone, or when the body’s sensitivity to these hormones changes, breast growth can occur. This imbalance can result from natural physiological changes or external factors affecting hormone levels.
Certain medications frequently trigger gynecomastia by altering hormone levels or interfering with hormone receptors. Antidepressants, heart medications, prostate medications, and anabolic steroids can all contribute to breast tissue development. Anti-anxiety medications, some antibiotics, and ulcer medications have also been linked to gynecomastia in susceptible individuals.
Underlying health conditions can disrupt normal hormone production and metabolism, leading to gynecomastia. Liver disease impairs the body’s ability to process estrogen, while kidney failure affects hormone clearance. Hyperthyroidism, testicular disorders, and certain tumors can also create hormonal imbalances that promote breast tissue growth.
Street drugs and substance use represent another significant category of gynecomastia causes. Marijuana use has been strongly associated with breast tissue development, while alcohol consumption can affect liver function and hormone metabolism. Anabolic steroid abuse, particularly when discontinued, can trigger a rebound effect leading to gynecomastia development.
What Is Pseudogynecomastia
Pseudogynecomastia, also known as the condition called pseudogynecomastia, refers to male breast enlargement caused exclusively by excess fat tissue accumulation in the chest area. In pseudogynecomastia, excess adipose accumulates around, behind, and under the nipples, leading to the appearance of enlarged male breasts. Unlike true gynecomastia, this condition involves no development of glandular breast tissue and results solely from an increase in adipose tissue deposits.
The texture of pseudogynecomastia differs markedly from true gynecomastia. The enlarged breasts feel soft and uniform throughout, similar to fatty tissue found elsewhere on the body. There is no firm, discrete mass beneath the nipple, and the tissue distribution is typically even across the entire chest area.
Men find that pseudogynecomastia typically develops gradually over time as overall body weight increases. The condition correlates directly with higher body fat percentages and often improves when patients successfully lose weight through dietary changes and exercise. Unlike gynecomastia, pseudogynecomastia rarely causes pain or tenderness.
The appearance of pseudogynecomastia tends to be more symmetrical than true gynecomastia, affecting both sides of the chest equally. The condition develops as part of overall weight gain and fat accumulation, making its presentation and distribution patterns more predictable.
Causes of Pseudogynecomastia
Weight gain serves as the primary cause of pseudogynecomastia, as excess fat tissue accumulates in various body regions, including the chest. Men with higher body fat percentages are more likely to develop noticeable chest enlargement due to the accumulation of fat in this area.
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in determining where individuals store excess fat tissue. Some men have a genetic tendency to accumulate fat in the chest region, making them more susceptible to developing pseudogynecomastia even with modest weight gain. This genetic factor explains why some men are more prone to developing chest fat than others.
Sedentary lifestyle and poor dietary habits contribute to fat accumulation and the development of pseudogynecomastia. A lack of regular exercise, particularly strength training that targets chest muscles, can lead to a loss of muscle. This is accompanied by an increase in fat tissue, resulting in a more pronounced appearance of breast enlargement.
Age-related metabolic changes affect how and where the body stores fat tissue. As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline, while metabolism slows. This leads to increased fat accumulation in areas previously lean. The chest area becomes more susceptible to fat storage as these hormonal and metabolic changes occur.
Key Differences Between Gynecomastia and Pseudogynecomastia
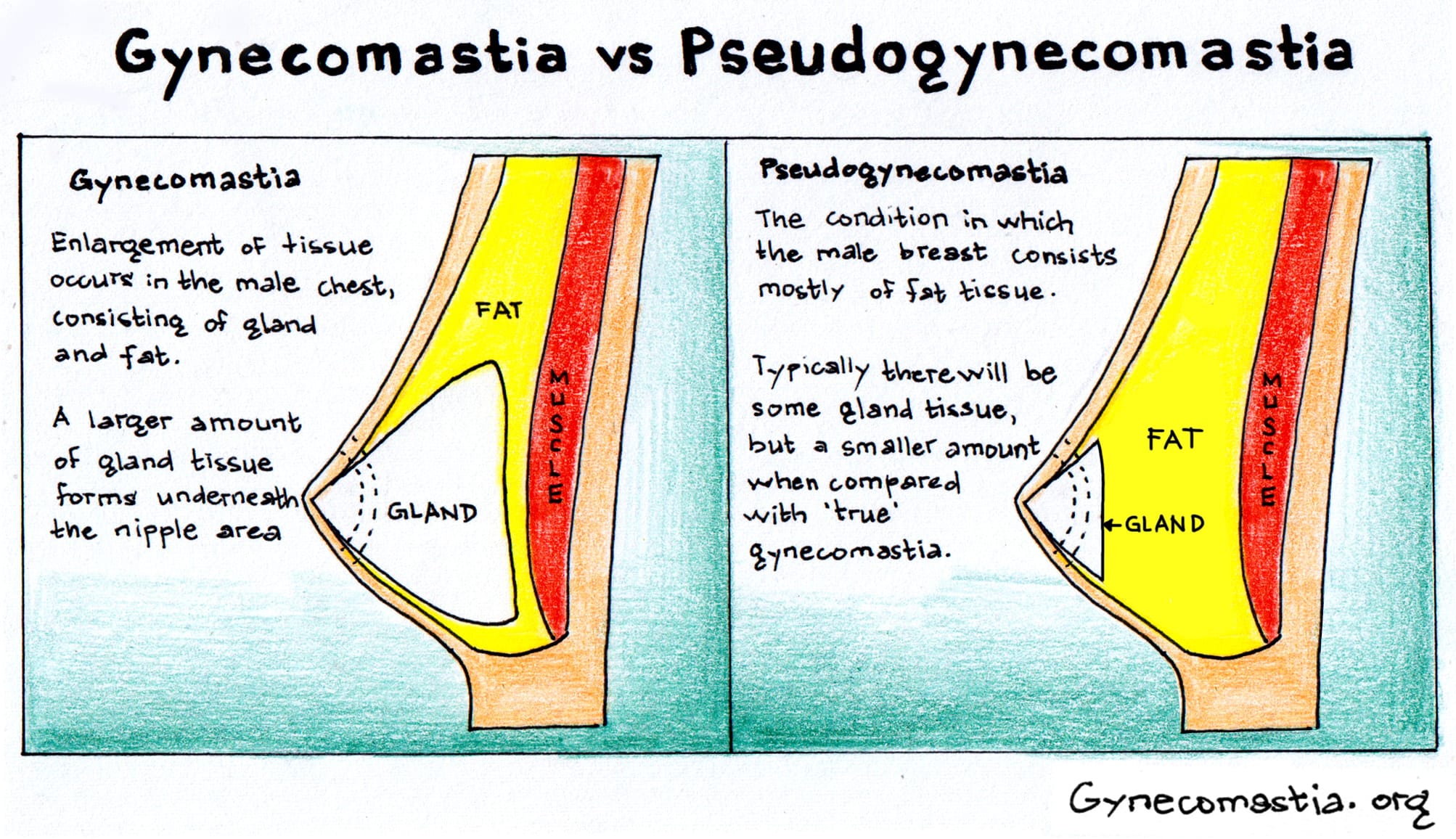
Understanding the key differences between gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia requires examining multiple factors. This includes tissue composition, physical characteristics, underlying causes, and treatment responses. The difference between gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia primarily lies in the cause of breast enlargement. Gynecomastia is due to excess glandular tissue, while pseudogynecomastia is due to excess fat. These distinctions are crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment plan for each individual case.
Characteristic | Gynecomastia | Pseudogynecomastia |
|---|---|---|
Tissue Type | Glandular breast tissue | Excess fat tissue |
Texture | Firm, rubbery | Soft, fatty |
Location | Concentrated under nipple | Distributed throughout chest |
Tenderness | Often present | Rarely present |
Response to Weight Loss | No improvement | May improve significantly |
Treatment Required | Surgical excision | Liposuction or lifestyle changes |
Physical Characteristics
The texture differences between these conditions provide the most reliable method for distinguishing gynecomastia from pseudogynecomastia during physical examination. Gynecomastia presents with firm, sometimes rubbery glandular tissue that can be distinctly felt beneath the nipple and areola. This tissue often forms a disc-shaped or nodular mass that feels different from surrounding fat tissue.
Pseudogynecomastia, in contrast, feels uniformly soft and fatty throughout the entire chest area. There is no discrete mass or firm tissue concentration, and the texture remains consistent with subcutaneous fat found elsewhere on the body. The tissue compresses easily and lacks the firm resistance characteristic of glandular tissue.
Location patterns also differ significantly between the two conditions. Gynecomastia typically concentrates the excess glandular tissue directly behind the nipple-areolar complex, creating a focused area of enlargement. Pseudogynecomastia distributes fat tissue more evenly across the entire chest, often extending toward the armpit and lower chest regions.
Symmetry patterns can help distinguish between conditions, though overlap exists. Gynecomastia frequently presents asymmetrically, with one breast developing more excess breast tissue than the other. Pseudogynecomastia tends to be more symmetrical, reflecting overall patterns of fat distribution throughout the body.
Response to Lifestyle Changes
The response to weight loss and exercise provides another key diagnostic tool for differentiating between gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia. Men with pseudogynecomastia may experience significant improvement in their chest appearance through dietary changes, cardiovascular exercise, and targeted strength training programs that focus on the chest muscles.
True gynecomastia shows little to no improvement with lifestyle modifications alone because glandular breast tissue cannot be reduced through diet and exercise. Even men who achieve significant overall weight loss will typically retain the firm glandular tissue characteristic of gynecomastia, requiring surgical intervention for optimal results.
Strength training can improve the appearance of both conditions by building underlying chest muscles, creating a more masculine chest contour. However, muscle development cannot eliminate excess glandular tissue in cases of gynecomastia, although it may help camouflage the condition to some degree.
Timeline expectations differ significantly between conditions. Men with pseudogynecomastia may begin seeing improvement within weeks of implementing lifestyle changes, with continued progress over months. Gynecomastia typically shows no meaningful response to these interventions, which helps confirm the diagnosis and the need for surgical treatment.
Diagnostic Methods and Professional Evaluation
Accurate diagnosis requires evaluation by a board-certified plastic surgeon or other qualified medical professional experienced in treating male breast enlargement. The diagnostic process begins with a comprehensive medical history and physical examination to assess tissue characteristics and identify potential underlying causes.
Physical examination techniques focus on palpating the chest area to distinguish between glandular tissue and fat tissue. The examiner will palpate for firm, disc-shaped masses beneath the nipple, which indicate true gynecomastia, while noting the overall texture and distribution of tissue throughout the chest area.
When the diagnosis remains unclear after physical examination, imaging studies may be recommended. Ultrasound can effectively differentiate between glandular tissue and fat tissue, showing distinct characteristics for each tissue type. Mammography may be used occasionally, particularly in older patients or when concerns exist about other underlying conditions.
Hormone level testing becomes necessary when gynecomastia is suspected, especially in cases involving rapid onset, significant asymmetry, or other concerning features. Blood tests can evaluate testosterone, estrogen, thyroid hormones, and other factors that might contribute to hormonal imbalance and breast tissue development.
Preparing for a consultation appointment involves gathering information about current medications, medical history, and the timeline of breast enlargement development. Patients should be prepared to discuss any associated symptoms, such as tenderness, nipple discharge, or changes in sexual function, that might indicate underlying hormonal issues.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia
Male breast reduction surgery represents the primary treatment for true gynecomastia, as excess glandular tissue cannot be reduced through non-surgical methods. The surgical approach varies depending on the amount of glandular tissue present and whether excess fat tissue coexists with the glandular component.
Surgical excision techniques focus on removing the firm glandular breast tissue through carefully placed small incisions. The most common approach involves making an incision along the lower edge of the areola, allowing the surgeon to access and remove the glandular tissue while minimizing visible scarring.
Many patients with gynecomastia also have some excess fat tissue in addition to the glandular component. In these cases, plastic surgeons often combine surgical excision of the glandular tissue with liposuction to remove excess fatty tissue and achieve optimal chest contour. This combined approach addresses all components of male breast enlargement.
Recovery from gynecomastia surgery typically involves wearing compression garments for several weeks to support healing and reduce swelling. Most patients can return to work within a week, though heavy lifting and intense exercise should be avoided for several weeks to ensure proper healing.
Surgical Techniques
The specific surgical excision technique depends on the amount and location of glandular tissue present. For smaller amounts of tissue, the surgeon may use a small incision technique that removes the glandular tissue through a minimal incision hidden at the edge of the areola.
More extensive cases may require larger incisions to completely remove all excess glandular tissue and achieve a smooth, masculine chest contour. In these situations, the plastic surgeon carefully plans incision placement to minimize visible scarring while ensuring complete tissue removal.
Liposuction often accompanies glandular excision to remove any excess fat tissue and create smooth transitions between treated and untreated areas. This combination approach helps achieve the most natural-looking results and addresses all components contributing to the enlarged appearance.
When significant amounts of excess skin exist in addition to glandular tissue, skin tightening procedures may be necessary. This typically occurs in cases involving substantial weight loss or long-standing gynecomastia, where the skin has stretched beyond its natural ability to contract.
Treatment Options for Pseudogynecomastia
Lifestyle modifications are the first-line treatment for pseudogynecomastia, as this condition results from excess fat tissue that can be potentially reduced through diet and exercise. Many patients achieve significant improvement without surgical intervention by implementing comprehensive fitness and nutrition programs.
Targeted chest exercises and strength training help build underlying chest muscles while promoting overall fat loss. Exercises such as push-ups, bench presses, chest flies, and dips can help strengthen the pectoral muscles and create a more defined chest contour as excess fatty tissue is reduced through overall weight loss.
Dietary changes to promote fat loss focus on creating a sustainable caloric deficit while maintaining adequate protein intake to preserve muscle mass. Working with a nutritionist can help develop an effective eating plan that promotes gradual and sustainable weight loss, while also improving overall body composition.
For stubborn fat deposits that persist despite lifestyle modifications, liposuction offers an effective surgical solution. This procedure removes excess fat tissue through small incisions, leaving the underlying chest muscles intact and creating a more contoured appearance.
Non-Surgical Approaches
Comprehensive fitness programs should include both cardiovascular exercise and strength training components. Cardio exercises help burn calories and promote overall fat loss, while strength training builds muscle mass and increases metabolic rate, supporting long-term weight management.
Nutritional counseling provides valuable support for men seeking to lose weight and reduce chest fat. Professional guidance helps ensure that dietary changes are sustainable and effective while meeting all nutritional needs during the weight loss process.
Body contouring treatments such as CoolSculpting represent non-invasive options for reducing localized fat deposits. While these treatments can help reduce fat tissue in the chest area, they typically require multiple sessions and may not achieve the dramatic results possible with liposuction.
Compression garments can provide temporary improvement in chest appearance by compressing fatty tissue and creating a smoother contour. While not a permanent solution, these garments can boost confidence during the weight loss process or for special occasions.
Mixed Cases: When Both Conditions Coexist
Many patients present with mixed cases involving both excess glandular tissue and excess fat tissue, requiring a comprehensive treatment approach to address all components of their male breast enlargement. These combination cases are actually quite common and require careful evaluation to develop an optimal treatment plan.
During consultation, experienced plastic surgeons assess the relative contribution of glandular tissue versus fat tissue to determine the most appropriate surgical approach. This evaluation influences the specific techniques used and helps set realistic expectations for surgical outcomes.
Tailored treatment plans for mixed presentations typically involve a combination of techniques. Surgical excision is used to remove glandular tissue, while liposuction addresses excess fatty tissue. This comprehensive approach ensures that all contributing factors are addressed for optimal results.
Comprehensive evaluation is especially important in mixed cases. Incomplete treatment can lead to suboptimal results and patient dissatisfaction. Surgeons must carefully assess all tissue types present and plan accordingly to achieve the desired masculine chest contour.
Recovery and Results
The timeline for healing after male breast reduction surgery varies depending on the specific procedures performed and individual healing characteristics. Most patients experience initial swelling and bruising that gradually subsides over the first several weeks following surgery.
Activity restrictions during the recovery period help ensure optimal healing and reduce the risk of complications. Patients typically avoid heavy lifting, strenuous exercise, and activities that might strain the chest muscles for 4-6 weeks after surgery.
Expected timelines for seeing final results extend several months beyond the initial surgery date. While initial improvement is visible immediately after surgery, final results become apparent as swelling resolves and tissues settle into their new contours over 3-6 months.
Long-term maintenance recommendations emphasize maintaining a stable body weight and engaging in regular exercise to preserve the surgical results. Significant weight gain after surgery can compromise results, particularly in cases where liposuction was performed to address excess fat tissue.
Signs of complications to watch for during recovery include excessive bleeding, signs of infection, persistent severe pain, or any concerning changes in the surgical sites. Patients should maintain close communication with their surgical team and report any concerning symptoms promptly.
Choosing the Right Treatment Provider
The importance of board certification in plastic surgery cannot be overstated when selecting a surgeon for male breast reduction procedures. Board-certified plastic surgeons have completed extensive training specifically in cosmetic and reconstructive surgery techniques.
Essential questions to ask during consultation include inquiring about the surgeon’s specific experience with gynecomastia surgery, their preferred surgical techniques, and their complication rates. Patients should also inquire about the surgeon’s approach to various types of cases and their philosophy regarding achieving optimal results.
Reviewing before-and-after photos provides valuable insight into a surgeon’s skill and aesthetic approach. Pay attention to cases similar to your own condition and assess whether the results align with your desired outcome and expectations for chest contour improvement.
Understanding costs and financing options helps patients plan for their treatment appropriately. Many plastic surgery practices offer financing plans to make treatment more accessible. It is essential to understand all the costs involved in the procedure and the recovery process.
Red flags to watch for when choosing a surgeon include those who are not board-certified in plastic surgery. Be cautious of anyone who guarantees specific results or pressures you to make immediate decisions without giving you enough time to consider your options.
Why choose Dr. Miguel Delgado from San Francisco for your gynecomastia surgeon?

Dr. Miguel Delgado is a highly experienced and respected board-certified plastic surgeon specializing in gynecomastia and male breast reduction surgery. Based in San Francisco, Dr. Delgado has dedicated much of his career to helping men achieve a more masculine chest contour through personalized, expert care. Patients choose him for his deep understanding of gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia. They also value his commitment to delivering natural-looking, long-lasting results.
One of Dr. Delgado’s key strengths is his ability to accurately diagnose the type and extent of male breast enlargement. He can clearly distinguish between excess glandular tissue and excess fatty tissue. This precision ensures that each patient receives a customized treatment plan tailored to their unique anatomy and goals. Dr. Delgado employs advanced surgical excision techniques, combined with liposuction when necessary, to effectively address both glandular and fatty components.
Patients appreciate Dr. Delgado’s compassionate approach and thorough consultations, where he explains the differences between gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia, discusses treatment options, and sets realistic expectations. His dedication to patient education helps men feel confident and informed throughout their treatment journey.
Dr. Delgado also prioritizes safety and minimizes scarring by utilizing small incision techniques whenever possible. His surgical expertise and attention to detail yield smooth chest contours and expedite recovery times. Many patients praise his ability to restore their self-esteem and quality of life by resolving the physical and emotional challenges associated with male breast enlargement.
Choosing Dr. Miguel Delgado means entrusting your care to a board-certified plastic surgeon with extensive experience in male breast reduction, a strong reputation for successful outcomes, and a genuine commitment to patient satisfaction. His San Francisco practice is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities, ensuring the highest standards of surgical care and comfort.
If you are considering treatment for gynecomastia or pseudogynecomastia, consulting with Dr. Delgado can provide you with the expert guidance and effective treatment plan you need to achieve a flatter, more masculine chest.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding the key differences between gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia is the first step toward finding the most effective treatment for enlarged male breasts. Both conditions can cause similar changes in chest appearance. However, the underlying causes differ. Gynecomastia involves excess glandular tissue, while pseudogynecomastia results from excess fatty tissue. Each requires a different treatment approach to achieve a more masculine chest contour.
For men dealing with true gynecomastia, male breast reduction surgery remains the most reliable and effective treatment. This procedure involves surgically removing excess glandular breast tissue. It is often combined with liposuction to address additional fat and sculpt a natural, masculine chest contour.
Pseudogynecomastia is caused by fat accumulation rather than glandular tissue. It often responds well to weight loss, strength training, and dietary changes. If stubborn fat remains despite these efforts, liposuction can provide a targeted solution to remove excess fat and refine the chest contour.
No matter which condition you are facing, consulting with a board-certified plastic surgeon is essential. A thorough evaluation by an experienced plastic surgeon will help determine whether your enlarged breasts are caused by excess glandular tissue, excess fat, or a combination of both. This expert assessment ensures your treatment plan is tailored to your unique needs. It also maximizes your chances of achieving the masculine chest contour you desire.
If you are considering male breast reduction or exploring treatment options for gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia, take time to research thoroughly. Choose a plastic surgeon with proven expertise in male breast surgery. Board certification, experience, and a strong track record of successful outcomes are key factors in selecting the right provider for your journey.
Remember, you do not have to live with the discomfort or self-consciousness caused by enlarged male breasts. With the right diagnosis and treatment, whether through surgery, lifestyle changes, or both, you can achieve a flatter, more confident chest. Start by scheduling a consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon. This is the first step toward a more comfortable and confident you.
FAQ
Can gynecomastia go away on its own without treatment?
Gynecomastia that develops during adolescence often resolves spontaneously within 6 months to 2 years as hormone levels stabilize. However, gynecomastia that persists beyond age 18 or develops in adulthood typically does not resolve without treatment. The glandular breast tissue that characterizes true gynecomastia cannot be reduced through lifestyle changes alone and typically requires surgical intervention for permanent resolution.
How long does it take to see results from pseudogynecomastia treatments?
Results from lifestyle modifications for pseudogynecomastia can begin appearing within 4-6 weeks of implementing consistent diet and exercise programs. Significant improvement typically becomes noticeable after 3 to 6 months of sustained effort. With surgical treatment using liposuction, initial results are visible immediately. Final results become apparent after 3 to 6 months, once the swelling has completely resolved.
What is the success rate of male breast reduction surgery?
Male breast reduction surgery has high success rates, with patient satisfaction exceeding 80-90% in most studies. Recurrence rates are below 10% when performed by experienced surgeons, particularly when underlying causes are addressed. Complications are rare, but can include bleeding, infection, changes in nipple sensation, or contour irregularities. Most patients achieve their desired masculine chest contour with permanent results.
Are there non-surgical treatments that can effectively treat true gynecomastia?
Medical treatments, such as selective estrogen receptor modulators or aromatase inhibitors, have limited effectiveness for established gynecomastia. They are rarely used outside of specific pediatric cases or early-stage presentations. These medications may help prevent progression in some cases, but cannot eliminate existing glandular tissue. Currently, surgical excision remains the most reliable method for effectively treating established gynecomastia.
How can I tell if I have gynecomastia or pseudogynecomastia at home?
While a professional evaluation is essential for accurate diagnosis, you can perform a basic self-assessment by gently feeling the chest area. Gynecomastia typically presents as a firm, rubbery disc of tissue directly behind the nipple, which feels different from the surrounding fat. Pseudogynecomastia feels uniformly soft and fatty throughout the chest area. However, mixed cases are common, and only a qualified medical professional can provide a definitive diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.
